Risk Management Ontologies
Risk Management Ontologies
Open Risk is supporting the development of semantic web technologies to support risk management efforts. This page organizes the currently developed / published tools. In principle any semantic technology can be the starting point for risk management ontologies. Open Risk adopts the W3C’s Web Ontology Language (OWL). OWL is a Semantic Web language designed to represent rich and complex knowledge about things, groups of things, and relations between things. OWL is a computational logic-based language such that knowledge expressed in OWL can be exploited by computer programs, e.g., to verify the consistency of that knowledge or to make implicit knowledge explicit.
OWL documents, known as ontologies, can be published in the World Wide Web and may refer to or be referred from other OWL ontologies. OWL is part of the W3C’s Semantic Web technology stack, which includes RDF, RDFS, SPARQL, etc
The Business Model Risk Ontology
The Business Model Risk Ontology is a framework that aims to represent and categorize knowledge about Business Models, in particular their Risk profile and
- Online Access
- Definition File
- Open Risk Manual Entry annotating the terms of the BMRO ontology
- A github repository with a python framework using the ontology to explore business model response to stress events
The Credit Ratings Ontology
The Credit Ratings Ontology is a framework that aims to represent and categorize knowledge about Credit Rating Agencies and related data (Credit Ratings) using semantic web information technologies.

- Online Access
- Definition File
- Open Risk Manual Entry annotating the terms of the CRO ontology
- An online course that uses the CRO ontology as an introductory example towards using Semantic Data
- A github repository with public ESMA ECAI data expressed using the ontology
The Non Performing Loan Ontology
The Non Performing Loan Ontology is a framework that aims to represent and categorize knowledge about non performing loans using semantic web information technologies.
- An introductory post about the NPLO ontology
- Online Access
- Definition File
- Open Risk Manual Entry: Non-Performing Loan
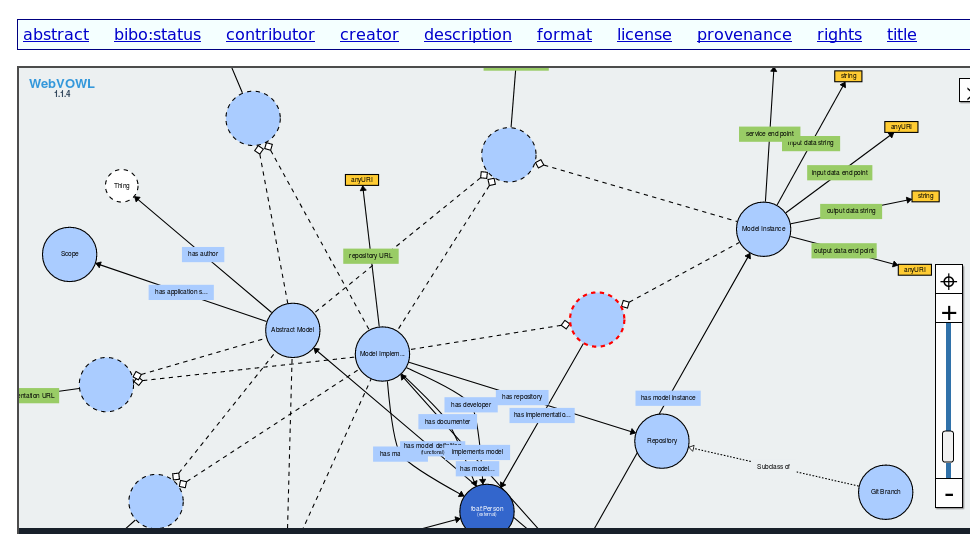
The Risk Model Ontology
The Risk Model Ontology is a framework that aims to represent and categorize knowledge about risk models using semantic web information technologies. The Risk Model Ontology, codenamed Description of a Model (DOAM) codifies the relationship between the various components of a risk model universe.
- An introductory post about the DOAM ontology
- Online Access
- Definition File
- Open Risk Manual Entry: Risk Model Ontology
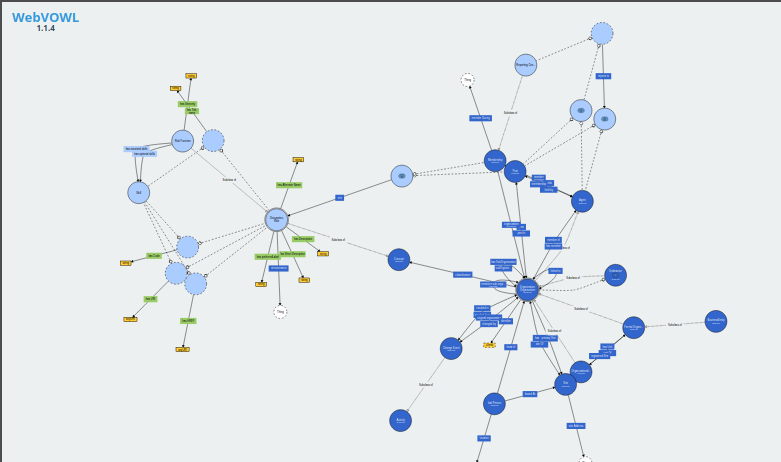
The Risk Function Ontology
The Risk Function Ontology is a framework that aims to represent and categorize knowledge about risk management functions. Codenamed RFO, it codifies the relationship (roles and responsibilities) between the various persons involved in a risk management organization.
The ontology allows the definition of risk management roles in more precise terms, which in turn can be used in a variety of contexts: towards better structured actual job descriptions, more accurate description of internal processes and easier inspection of alignement and consistency with risk taxonomies
- An introductory post about the RFO ontology
- Online Access
- Definition File
- Open Risk Manual Entry: Risk Function Ontology