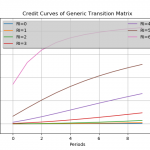
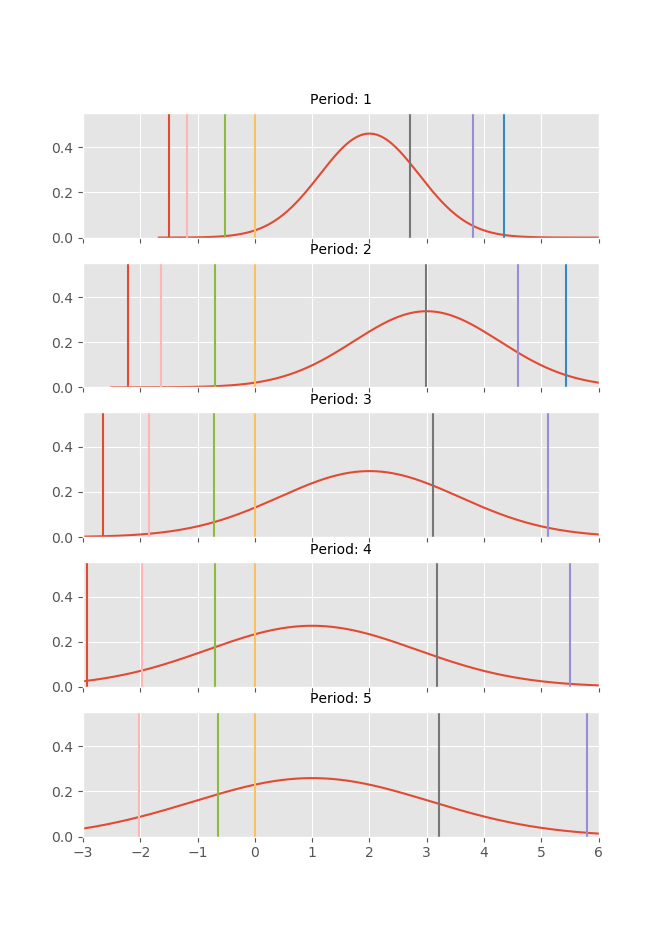
Stressing Transition Matrices
Release of version 0.4.1 of the transitionMatrix package focuses on stressing transition matrices
Further building the open source OpenCPM toolkit this realease of transitionMatrix features:
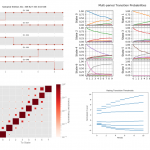
- Feature: Added functionality for conditioning multi-period transition matrices
- Training: Example calculation and visualization of conditional matrices
- Datasets: State space description and CGS mappings for top-6 credit rating agencies
Conditional Transition Probabilities
The calculation of conditional transition probabilities given an empirical transition matrix is a highly non-trivial task involving many modelling assumptions. This version of the transitionMatrix includes a canonical implementation that assumes a Gaussian single factor process as the driver of the joint rating dynamics. The technical documentation is available under in Open Risk Manual under the transition matrix category.