Connecting the Dots, Tensor Representations of Activitypub Networks
Connecting the Dots, Tensor Representations of Activitypub Networks
What are ActivityPub Networks?
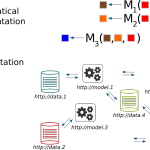
ActivityPub is a technical specification towards decentralized (more precisely, federated) social networking (termed the Fediverse) based upon the exchange of ActivityStreams messages that follow the Activity Vocabulary. The ActivityPub proposal has been standardized and published by the W3C and has motivated the design of several federated social networking systems.