EEIO in Sustainable Finance
EEIO in Sustainable Finance - Challenges and Opportunities. This is a Presentation given given at the 15th I-O Workshop, March 1st 2024, Osnabruck, Germany.
EEIO in Sustainable Finance: Challenges and Opportunities
Presentation given at the 15th I-O Workshop, March 1st 2024, Osnabrueck, Germany
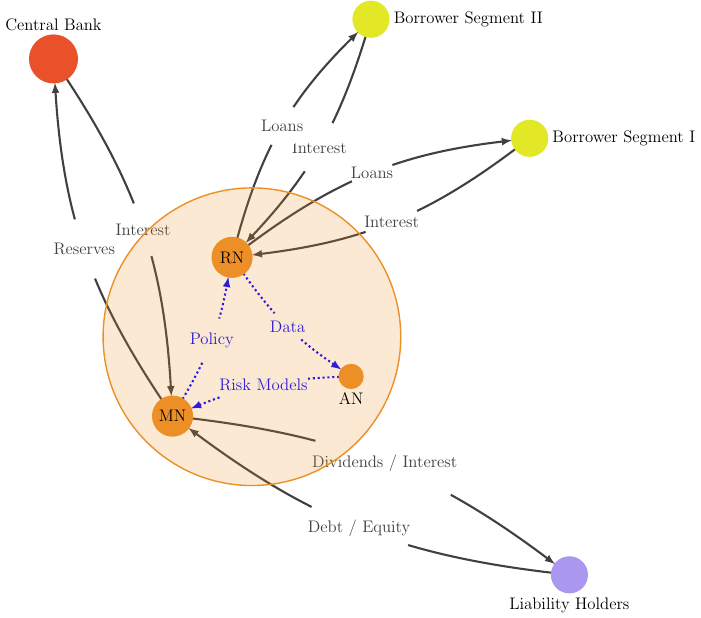
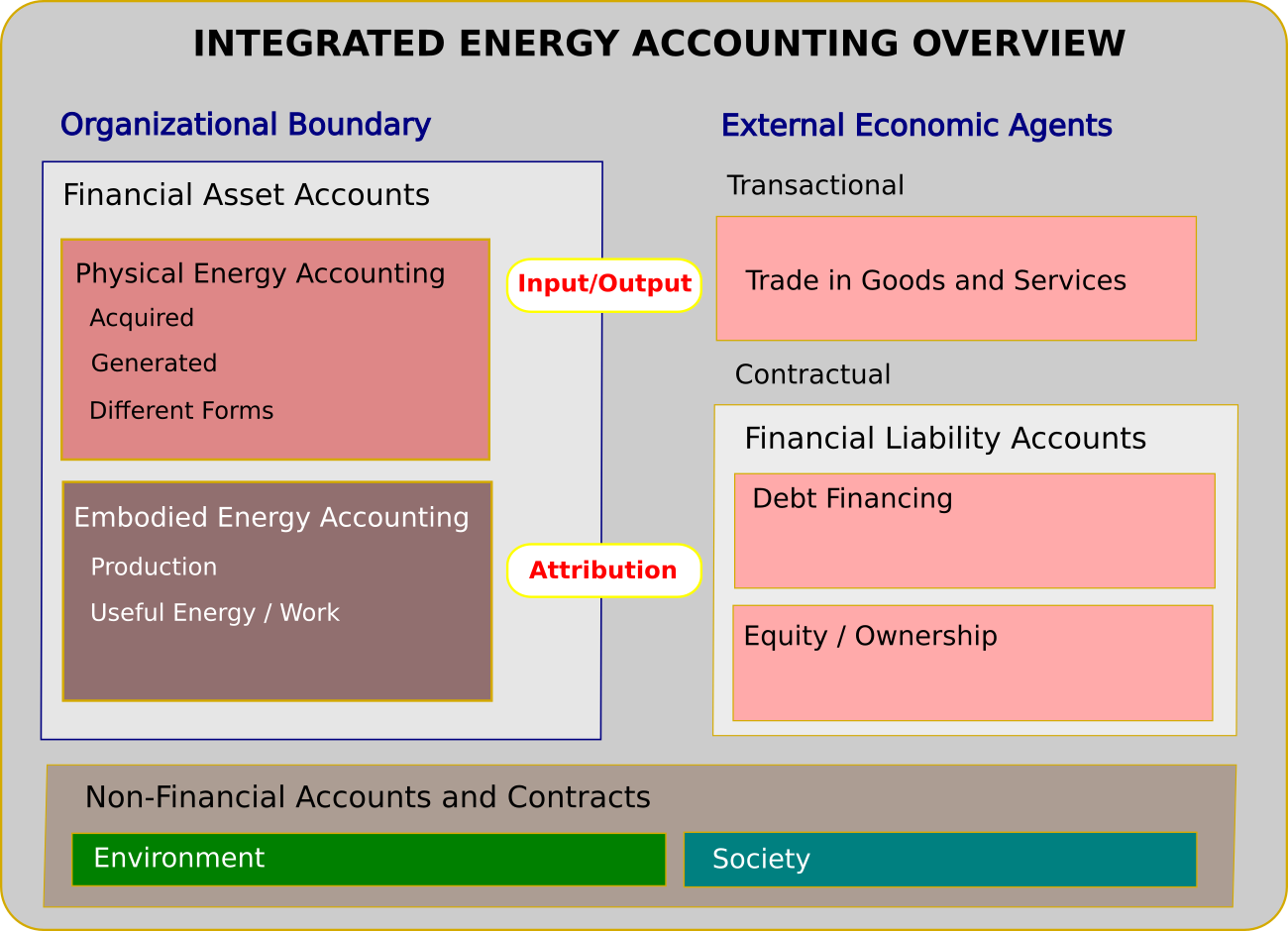
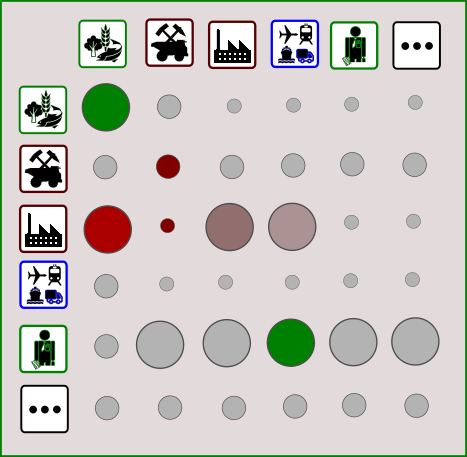
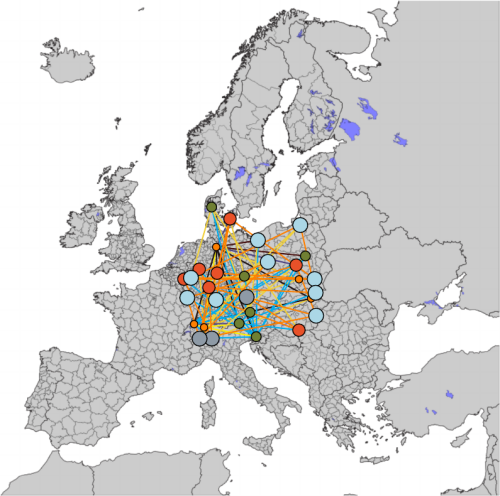
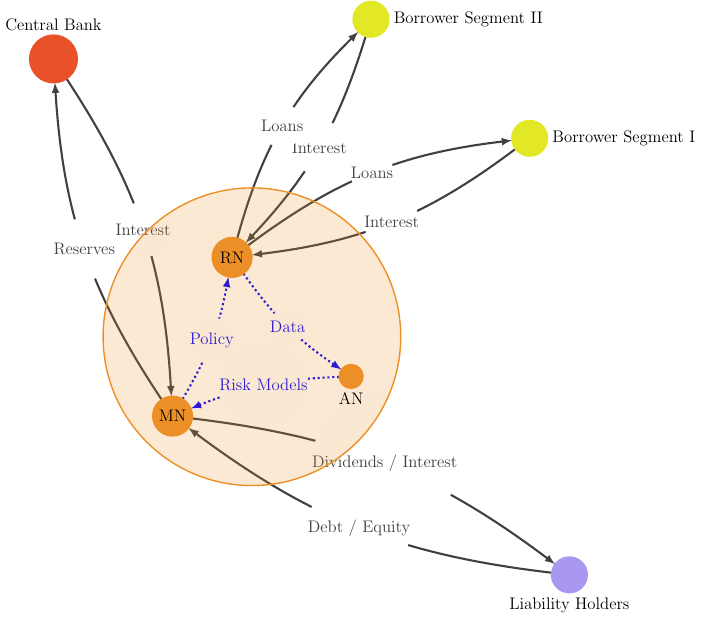
We discuss the overlap of EEIO tools with Sustainable Finance applications. In particular their potential role in Portfolio Management and, more specifically,
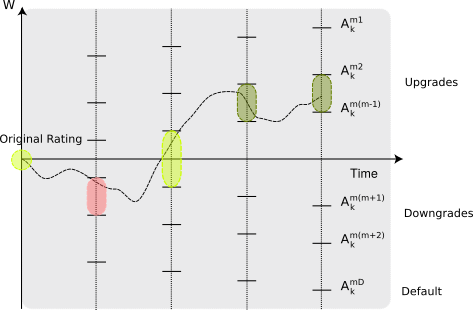
- the Attribution of environmental impact in financial portfolios and,
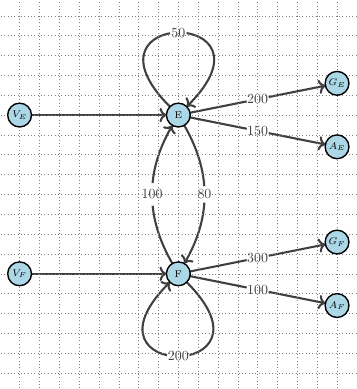
- the Allocation of future financial resources and sustainability constraints
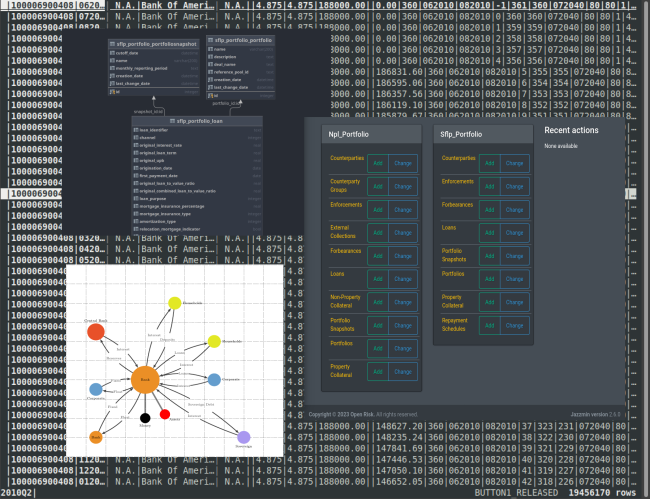
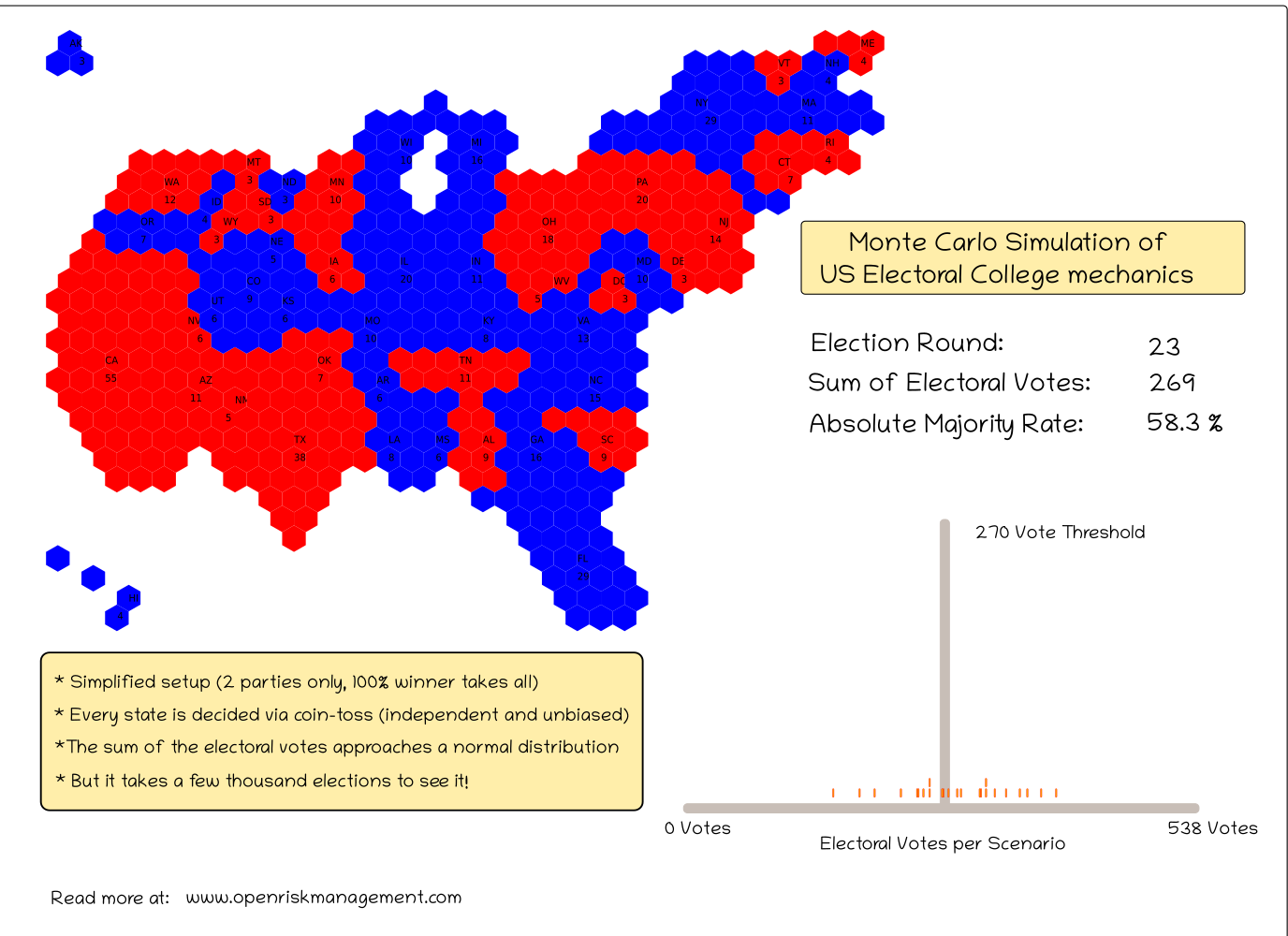
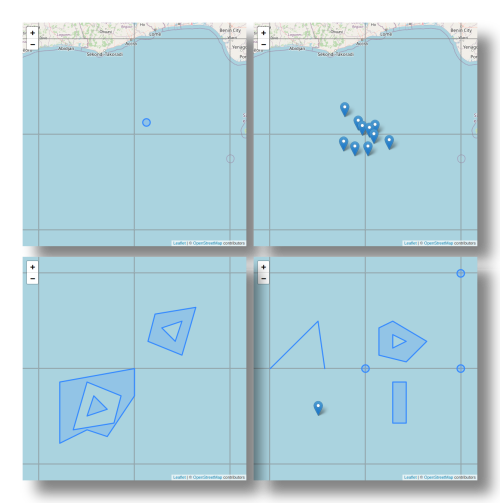
We sketch two proof-of-concept computer applications that highlight opportunities and challenges: