An introduction to Semantic Python
A CrashCourse introduction to semantic data using Python covering a number of frameworks such as rdflib, owlready and pySHACL
This CrashCourse is an introduction to semantic data using Python.
Course Content
It covers the following topics:
- We learn to work with RDF graphs using rdflib
- We explore the owlready package and OWL ontologies
- We look into json-ld serialization of RDF/OWL data
- We try data validation using pySHACL
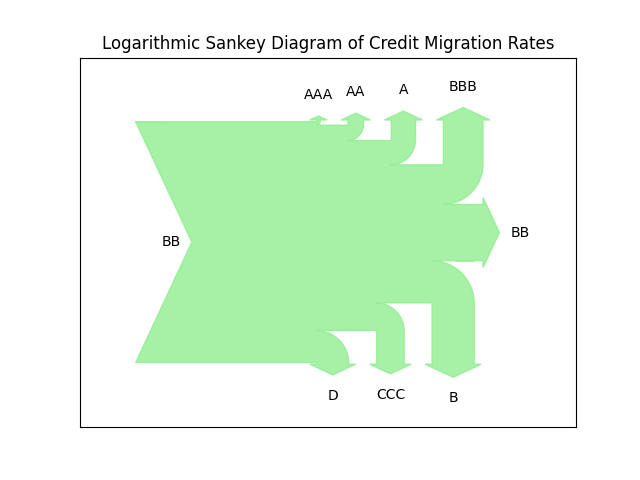
- We use throughout a realistic data set based on the Credit Ratings Ontology